Supply Chain Management
Principles and System of Supply Chain Management
To build a supply chain that is sound and sustainable, Tokyo Electron has formulated a procurement policy based on the laws, regulations and social norms of each country, as well as the RBA Code of Conduct, and together with its suppliers, is implementing activities based on this policy. To identify issues in the supply chain from a variety of perspectives, we also value ongoing communication with diverse suppliers, including materials suppliers that handle parts and raw materials, staffing suppliers that provide services and logistics suppliers that handle physical distribution operations. Any issues which are identified are shared among the relevant departments which then work on improvement measures, under the supervision of the CEO. We will continue striving to create value across the supply chain by working to build relationships of trust with our suppliers, who support our business as partners, and by working together to deploy our operations in compliance with global standards.
The high-value manufacturing that the Tokyo Electron Group strives for is based on the functions of all materials and components that make up the products and the pursuit of high quality. We value communications with suppliers and seek to grow manufacturing on a global scale with our suppliers based on ongoing trusting relationships.
- Compliance with Applicable Laws, Social Norms, and the RBA Code of Conduct
- We engage in procurement activities based on business ethics and with integrity, in compliance with the laws, regulations, and social norms of each country as well as the RBA Code of Conduct.*
The RBA Code of Conduct: Responsible Business Alliance Code of Conduct
https://www.responsiblebusiness.org/code-of-conduct/
A code of conduct drawn up by the RBA. The RBA Code of Conduct establishes standards to ensure that working conditions are safe, that workers are treated with respect and dignity, and that business operations are environmentally responsible and conducted ethically. - Priority on the Environment
- We conduct procurement with full consideration for reduction of environmental impact and protection of the global environment.
- Fair Business Practices
- We continuously seek high-value technologies and create broad opportunities for their business transactions based on the precondition of open competition.
- Partnership
- We prioritize relationships of trust based on mutual understanding with suppliers and conduct activities in the pursuit of mutual continuous growth.
- Information Management
- We properly manage the confidential information of suppliers that we obtain in the course of business
The Tokyo Electron Group aims for sound and sustainable growth together with suppliers to contribute to the development of society. We will strive to achieve this, with the cooperation of our suppliers. We therefore request your active efforts in the following matters.
- Compliance with Applicable Laws, Social Norms, and the RBA Code of Conduct
In addition to complying with the following matters, we ask our suppliers to observe the applicable laws and social norms in the countries and regions where they engage in business, as well as the RBA Code of Conduct.
- Compliance with prohibition of child labor, and forced labor, and with other labor-related laws and regulations
- Respect for fundamental human rights, beginning with the prohibition of discrimination
- Protection of intellectual property rights
- Compliance with export/import-related laws and regulations
- Prohibition of involvement with antisocial forces
[Conflict minerals] We see our efforts with regard to conflict minerals as part of our corporate social responsibility, and promote all efforts to eliminate any use of raw materials that utilize conflict minerals which have been mined or extracted with illicit funds or by illegal methods, as well as components or parts that contain such conflict minerals. To this end, we are conducting due diligence surveys of our supply chain, using the Conflict Minerals Reporting Template (CMRT) and referring to the OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains of Minerals from Conflict-Affected and High-Risk Areas. We request that all suppliers work with us in dealing with conflict minerals.
- Working Conditions
- We request that suppliers respect fundamental human rights, also prepare independent standards, and provide safe and healthy work environments.
- Environmental Activities
- In accordance with "Tokyo Electron Green Procurement Guidelines", we request that, together with the acquisition of ISO 14001 and the development of a structure for environmental conservation, suppliers also actively engage in environmental conservation activities and strive to use parts and materials, and methods of production, that have a reduced environmental impact and that consider resources conservation.
- Management System
- We request that management systems are developed and continuously improved, including systems related to safety, health, the environment, product quality and labor, in accordance with the corporate procurement agreement or any specific agreements or arrangements with the Tokyo Electron Group.
- Technical Skills
- We request that, in order to provide products and services that conform to customers' needs, suppliers always strive for improved technical skills and technological innovations.
- Quality
- We request that suppliers provide high-quality products and services which meet the specifications required by the Tokyo Electron Group, by means of building quality during the design phase, and strengthening change control.
- Supply, and Provide Systems
- We request that suppliers provide a stable and flexible supply of products and services to deal with huge volatility in demand. Also, we request that suppliers prepare precautionary steps and continuity plans to reduce risks in the event of unforeseen situation such as disaster.
- Price
- We request that products and services are offered at competitive prices, and that continuous effort is made to reduce costs.
- Business Management
- For the continuation of our business transactions, we ask that sound and stable business management be implemented. We also request that the financial and company information needed to confirm those matters is disclosed.
- Information Security
- We request that a system be provided which prevents the leaking of confidential information and that any information acquired in dealings with the Tokyo Electron Group is strictly controlled.
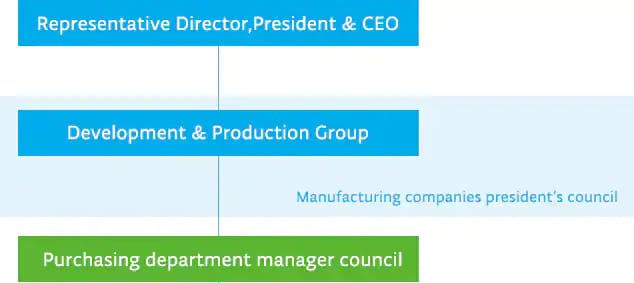
To maintain a robust supply chain capable of supporting streamlined product manufacturing, TEL has instituted a procurement policy and established a system for administering fair procurement practices based on mutual trust with suppliers. Under the TEL Representative Director and President as the top of the procurement system, the manufacturing companies presidents’ council and the purchasing department manager council are convened to share information on various procurement issues. The council also serves as a venue to address current problems and discuss approaches to improve partnership with suppliers.
Initiatives in the Supply Chain
Sustainability Operations
To keep track of our suppliers’ engagement in sustainability, we conduct an annual sustainability assessment in areas such as labor, health and safety, the environment and ethics since fiscal year 2014. We analyze the assessment results, provide feedback to suppliers and ask them to carry out any improvement activities required. In fiscal year 2019, we completely revised the content of the assessment based on audit standards stipulated by the RBA, and in addition to materials*1 suppliers, included staffing*2 and logistics*3 suppliers in the scope of the assessment.
In fiscal year 2023, we had Tokyo Electron Technology Solutions (Yamanashi), one of our main manufacturing sites in Japan, undergo RBA auditing, and have carried out the necessary remediation activities together with our suppliers. Going forward, we will further promote compliance with industry codes of conduct through having our other major manufacturing sites undergo similar auditing, including those located overseas, and will expand sustainability initiatives throughout the supply chain.
In addition, to promote these initiatives and support supplier’s efforts, we conducted briefings on RBA Code of Conduct and audit standards to personals in charge of supply chain management.
To ensure that all people in our supply chain can work of their own free will, we have expressly stipulated our zero-tolerance policy for forced labor and bonded labor, and have communicated this to our major suppliers.
Supply Chain Sustainability Process

Materials suppliers: Assessment has been conducted for suppliers accounting for more than 80% of our procurement spend (85% from fiscal year 2023)
Staffing suppliers: Assessment has been conducted since fiscal year 2019 on 100% of employment agencies and contracting companies (internal contractors).
Logistics suppliers: Assessment has been conducted since fiscal year 2019 on 100% of customs-related operators.
Responsible Procurement of Minerals (Conflict Minerals)
We see taking action against conflict minerals (3TG*1) obtained through illegal exploitation, which lead to human rights violations and poor working conditions, as our corporate social responsibility. Our resolute goal is to eliminate the use of raw materials made from these conflict minerals, as well as any parts or components containing them. In alignment with this way of thinking, we conduct surveys on potential conflict minerals using the CMRT*2 and referring to the OECD*3 Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains of Minerals from Conflict-Affected and High-Risk Areas. In fiscal year 2023, we conducted our ninth annual survey on potential conflict minerals. As a result, we were able to identify 234 smelters conformant with RMAP*4 (one of the standards used for determining whether minerals are connected with conflict). In addition, none of the materials we procured were found to contain 3TG involved in conflict.
3TG: Tantalum, tin, tungsten and gold
CMRT: Conflict Minerals Reporting Template. Survey format for reporting conflict materials, provided by the Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI), which has established international guidelines on conflict minerals.
OECD: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
RMAP: Responsible Minerals Assurance Process. A program promoted and led by the RMI for auditing smelters/refiners to validate that they do not use conflict minerals.
Procurement BCP
As part of our business continuity plans (BCPs), we collaborate with suppliers on ongoing disaster preparation. We maintain a database of suppliers’ production sites so that if a crisis arises, we can promptly identify impacted suppliers and quickly collaborate in recovery efforts. There are now approximately 30,000 registered production sites as of fiscal year 2023, and post-disaster impact assessments (conducted when disasters occur) have been implemented five times. In addition, we conduct BCP assessments on our suppliers and analyze their responses to provide them with feedback so that they can promote improvements in areas of concern.
BCP assessment: Surveys have been conducted since fiscal year 2013 on suppliers accounting for more than 80% of our procurement spend.

Supply Chain Communication
Cooperation with Suppliers
In addition to daily communications, we hold Production Update Briefings and a TEL Partners Day to enhance relationships with suppliers. At these events, we present and exchange information on the management plans, market trends, business policies, and CSR initiatives. We also ask for continued cooperation in strengthening our supply chain, and honor outstanding suppliers to express our appreciation for their constant support.
In addition, we award "Environmental Partners" and recognize "The Green Partners" to suppliers who offer outstanding cooperation and contributions to our environmental activities through E-COMPASS initiatives.

Before starting business with new suppliers, an STQA is conducted via self-assessment to evaluate their product quality, costs, and information security. The assessment also includes CSR issues, including human rights, ethics, safety, and the environment. If any risks to quality are found, we visit the supplier on-site to explain the problems, our expectations for improvement, and the level of quality we require. After the supplier understands the issues, we ask that they plan and implement improvement measures. We also offer continual support to suppliers until all necessary improvements have been made. We conduct on-site audits once every three years at suppliers who manufacture important components and at suppliers where quality issues have been found.
We focus on the change control education with our suppliers. We aim to reduce the number of quality issues that occur as a result of changes to the design or manufacturing of equipment components and modules. We also aim to reduce the cost of quality improvements. We conduct briefings for suppliers to explain matters such as the importance of change control, and have conducted online training since fiscal year 2016.
In addition, Tokyo Electron announced the “Declaration of Partnership Building” in September 2022 to support the purpose of the Council on Promoting Partnership Building for Cultivating the Future, and in February 2023 Tokyo Electron Technology Solutions, Tokyo Electron Kyushu and Tokyo Electron Miyagi also announced, that is promoted by the Cabinet Office, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI), the Small and Medium Enterprise Agency (SMEA), and others.

Supplier Case Studies
Aside from the assessment program described above, Tokyo Electron Kyushu cooperates with suppliers to implement initiatives to reduce the occurrence of defective goods. We visit the production sites of suppliers to learn about their production environment whereby they are able to provide effective improvement proposals. We conduct process analysis together with suppliers to build better processes whereby we promote steady reduction of defects, creating win-win relationships for improved productivity.
Cooperation with industry organizations
In June 2015, TEL joined the RBA*. RBA participation includes adopting the RBA Code of Conduct, a set of standards to improve labor practices, health and safety, environmental impact, and ethics in supply chain. TEL adheres to the RBA Code of Conduct to maintain and strengthen its supply chain, in cooperation with other RBA member companies.
RBA: Responsible Business Alliance

