Learn about semiconductors
Semiconductors are vital to the development of a dream-inspiring society.
Below, we will answer some frequently asked questions about semiconductors.




Question 01
What are the uses of semiconductors?
Semiconductors are used in all kinds of electronics ranging from smartphones to satellites.
Semiconductors are used everywhere. They are not only found in the smartphones, personal computers, home appliances, and automobiles that we use every day, but also in artificial satellites orbiting the earth. In fact, semiconductors are indispensable to electronic devices and appliances on which our way of life and the industry heavily depend.




Question 02
How large is the global market for semiconductors?
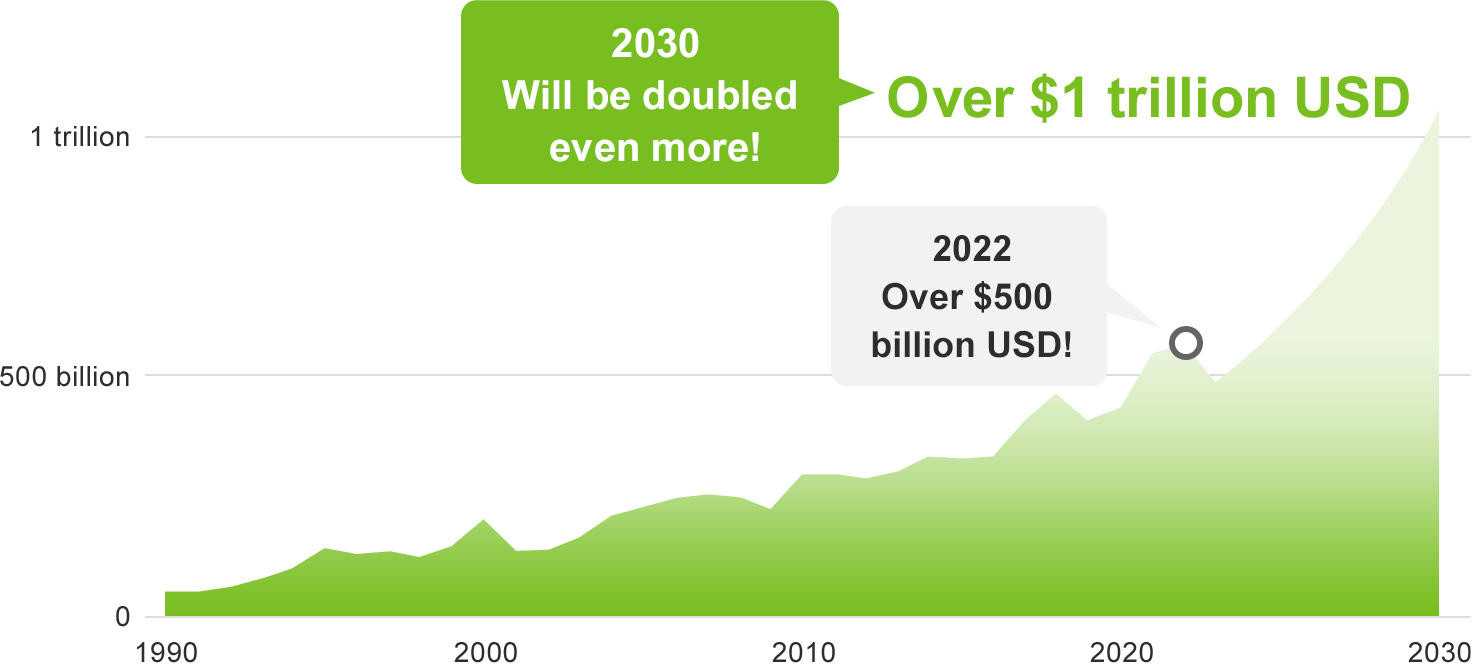
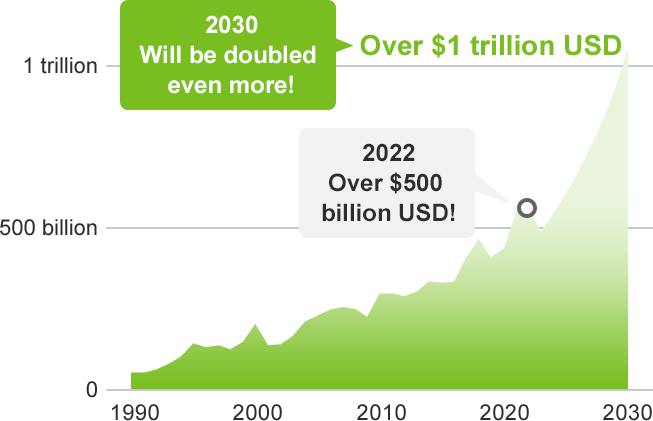
The size of the semiconductor market is currently in excess of $500 billion USD and is expected to double by 2030.
The production volume of semiconductors is rising every year due to the acceleration of society’s digitalization. The market size of semiconductors exceeded $500 billion USD in 2022 and is expected to double by 2030 to over $1 trillion USD.



Question 03
What is a semiconductor?
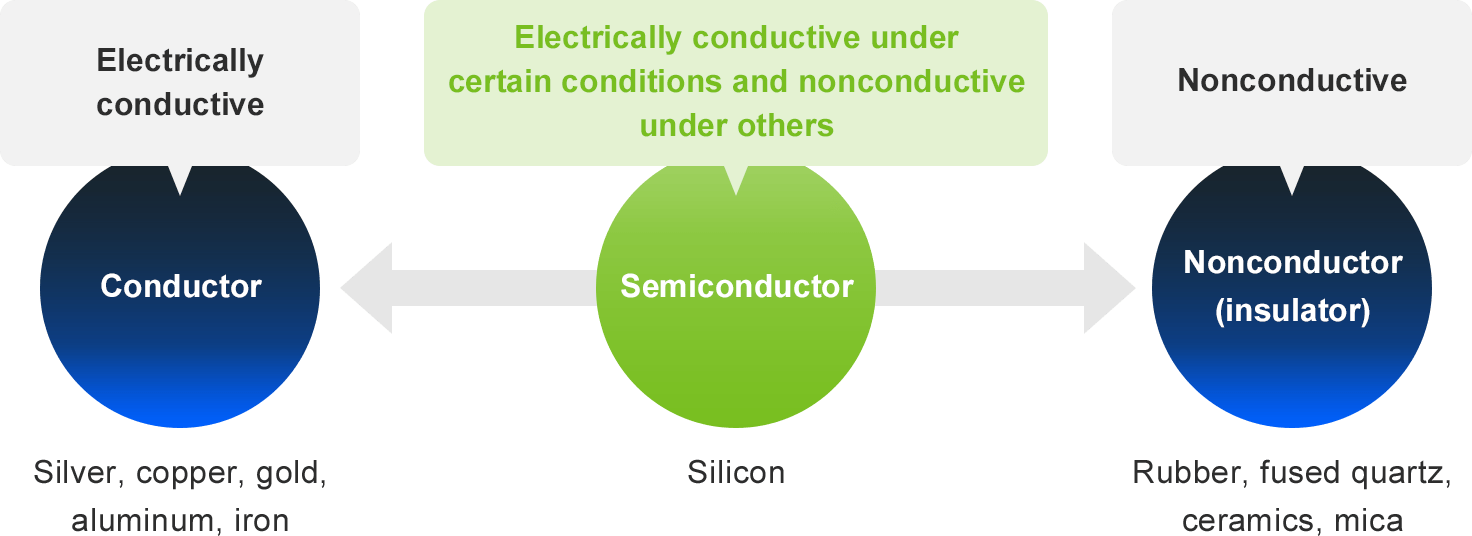
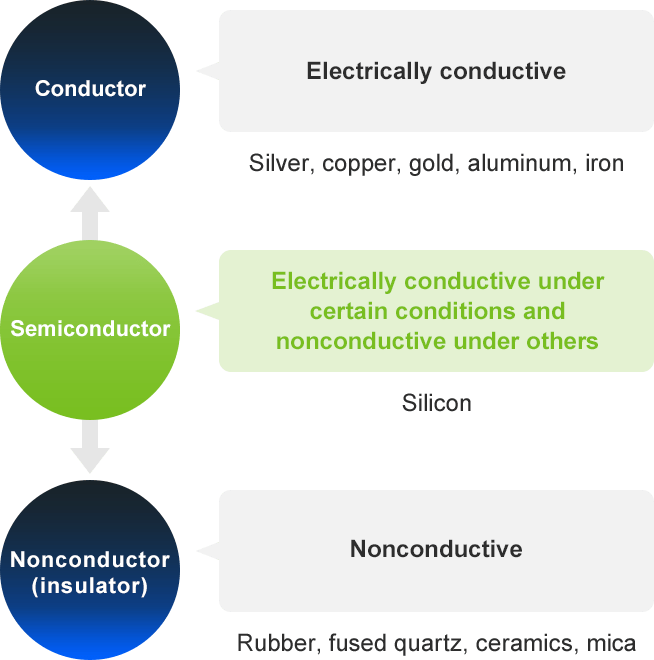
A semiconductor is a material that can act like an electrical conductor or a nonconductor depending on certain conditions. Electronic circuit components that utilize these properties (semiconductor devices) are also referred to as semiconductors.
Materials that allow electricity to flow through them (such as metals) are known as conductors, and those that hardly let electricity flow through them (including rubber) are called insulators. A semiconductor has a conductivity value between these two opposites: it is electrically conductive under certain conditions and nonconductive under others. Because of these properties, semiconductors make excellent electrical switches, enabling computers and other devices to perform complex data processing tasks.




Question 04
What are the roles and applications of semiconductors?
Semiconductors store information, calculate numerical data, and play a principal role in a wide range of electronic devices.
When used as components of electronic circuits, different kinds of semiconductors assume different roles, depending on their types. Some are used to process information just as a human brain does while others are employed to store huge amounts of information or capture imaging data. Depending on their roles, the required structures of semiconductor devices vary significantly, and the production technologies are just as diverse.
Examples of semiconductors in a smartphone
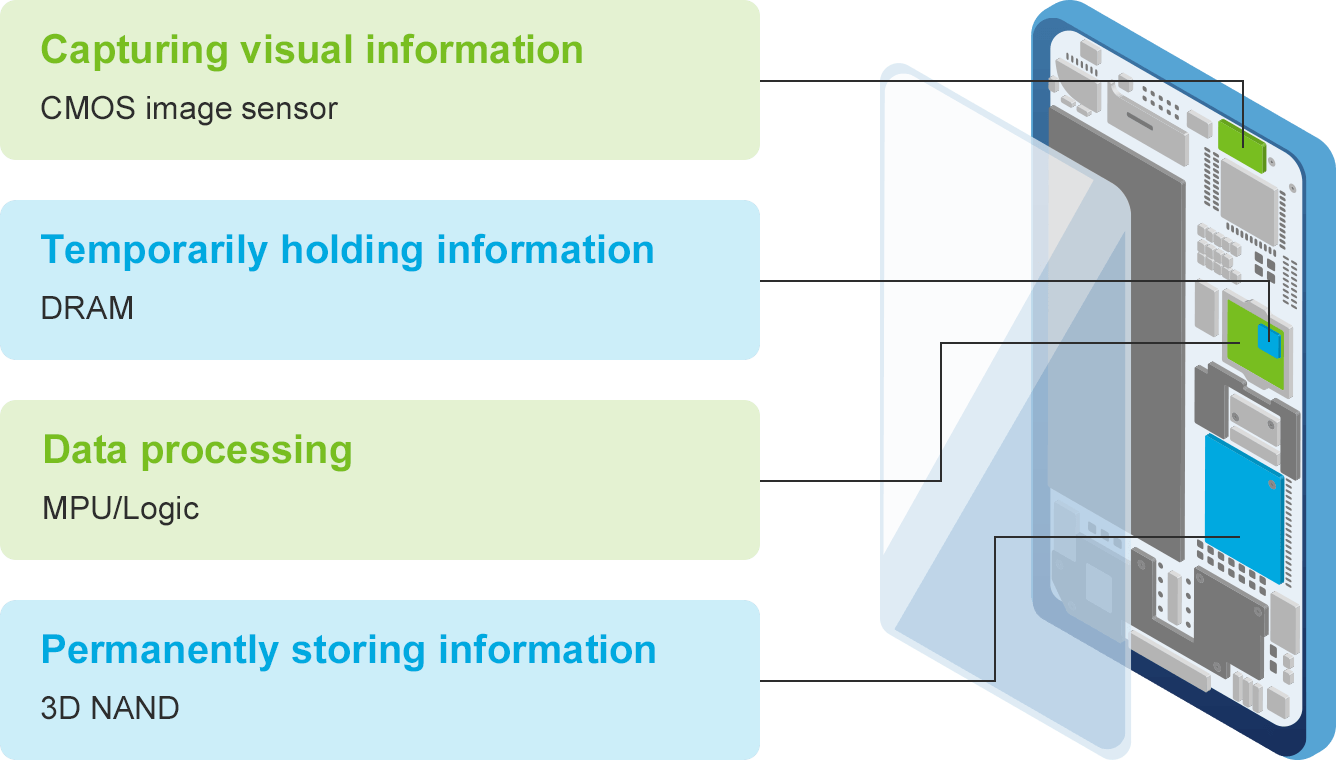
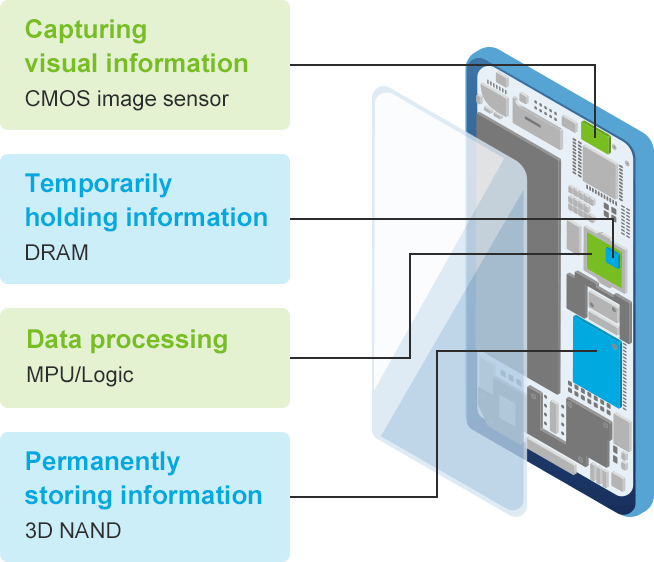






Question 05
Will semiconductors continue to evolve?
Semiconductors are continuously evolving in response to demand for larger capacity, higher speed, superior reliability, and lower power consumption.
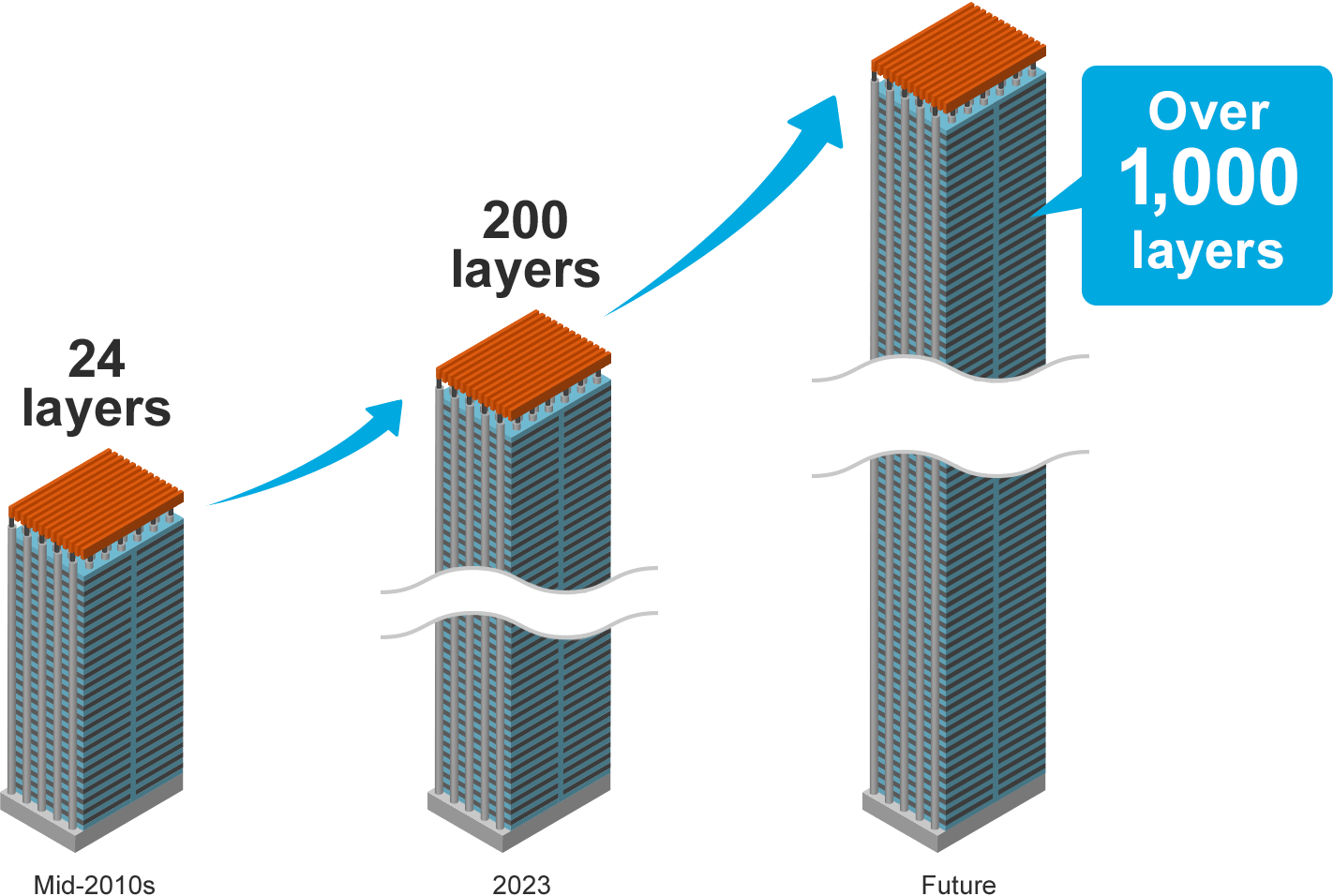
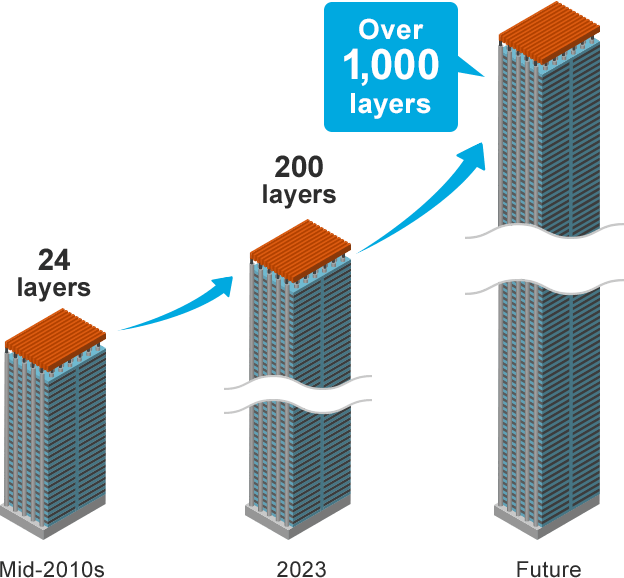
Higher performance is repeatedly demanded of the semiconductors that form the foundation of all advanced technologies. Currently, the most advanced semiconductors have entered the domain of nanometers (1 nanometer = one billionth of a meter), and even further scaling is being explored. Take NAND flash memory, for instance. Commonly used to store data in PCs and smartphones, NAND flash memory chips feature an increasing a number of layers of memory cells stacked on top of each other, an innovation that allows the cells to be packed more densely on a substrate. The number of layers in the advanced chips exceeded 200 in 2023 and our roadmap envisions to exceed 1,000 in the future to address the need for ever higher memory capacity.
Trend of technological innovation in NAND flash memory stacking








Question 06
How will our world change as semiconductors become more advanced?
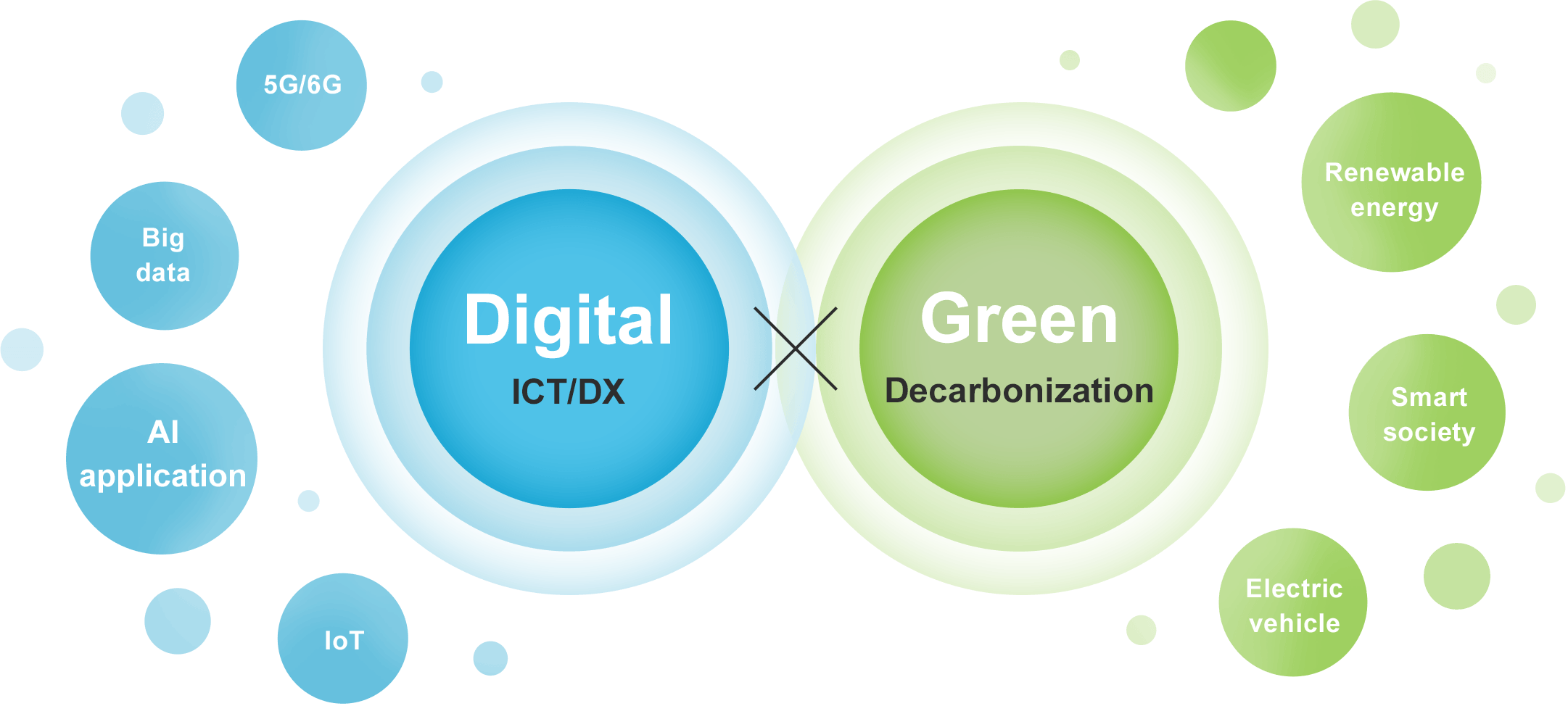
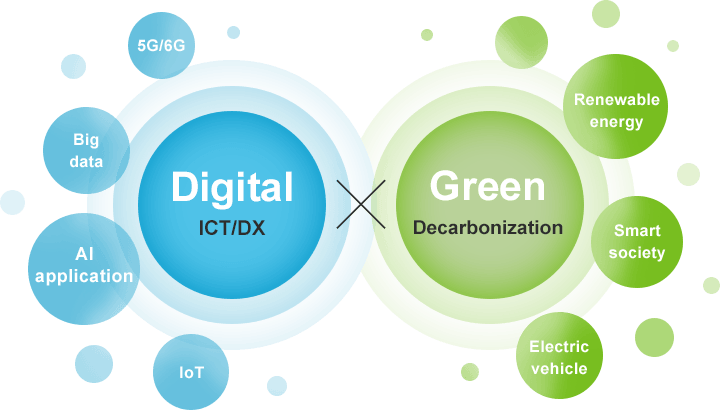
Advanced semiconductors will support the development of society through digitalization and preservation of the global environment through decarbonization, bringing us closer to the coexistence of a “Digital x Green” world.
New technologies that enable the development of modern society— such as AI, advanced data center platforms, and quantum computing—cannot exist without continual innovation in semiconductors. In addition to enhancing the capacity, speed, and reliability of semiconductors, the environmental impact must also be reduced in the pursuit of lower power consumption. Expectations are rising for advanced semiconductors as the key infrastructure to build a strong, resilient, and sustainable society.
Semiconductors enable a dream-inspiring society, and Tokyo Electron holds the key to making such technological innovations possible.
Virtually almost all semiconductors in the world today go through TEL’s equipment in their production sequence.
On an invisible level, our innovative technologies are shaping the future of the world.
To find out more about semiconductors, please refer to the following resources.
Nanotech Museum
A website that explains the principles and history of nanotechnology
-

The Principle of Semiconductor
Basic facts about semiconductors explained in detail, along with glimpses into their progress and applications
-

The history of Semiconductor
An overview of the evolution of semiconductors from the invention of the vacuum tube to the present day
-

How a Semiconductor is made
An introduction to various processes of semiconductor manufacturing and the equipment designed to perform respective processing steps
TELESCOPE Magazine
TEL’s journal covering the latest advancements in semiconductors and other topics in science and technology